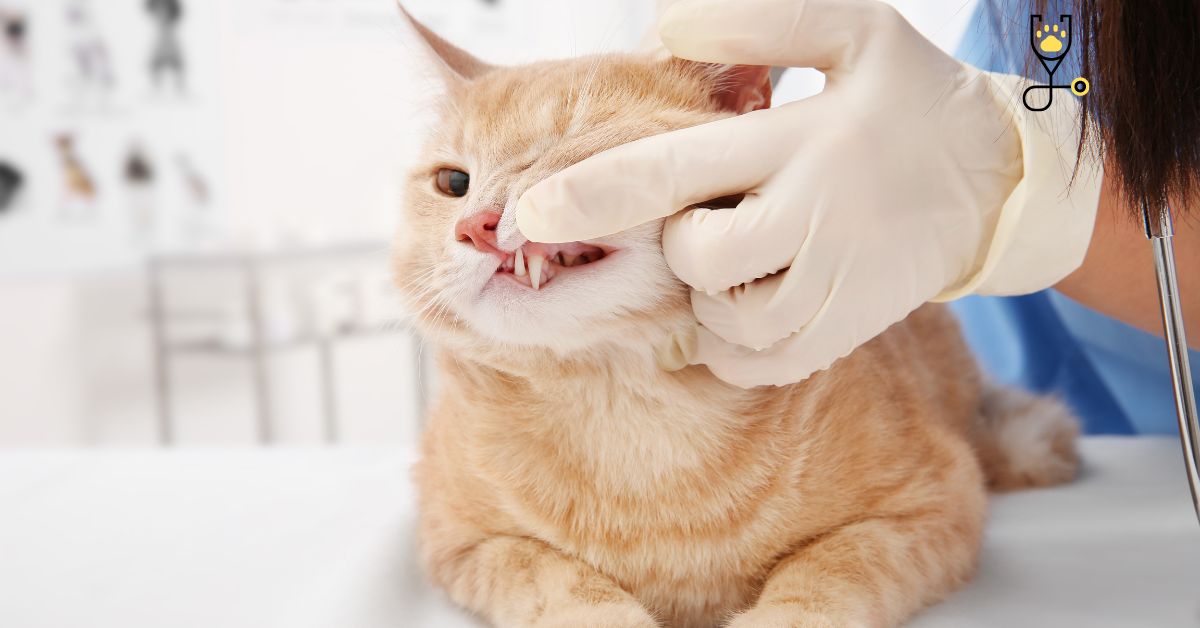
Did you know that one in three cats will develop some form of gum disease in their lifetime? And, while it is most common in older cats, gingivitis can occur at any age. In this post, we’ll take a look at what causes gingivitis in kittens, the symptoms to watch for, and how to treat and prevent it. So keep reading for all the info!
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums and is the early stage of periodontal disease. Gingivitis is usually caused by plaque build-up on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If not removed, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which can lead to gum disease. Gingivitis is a reversible condition, meaning it can be treated and reversed if caught early. However, if left untreated, it can progress into periodontitis, which is a more serious form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss.
Causes of Gingivitis in Kittens
The most common cause of gingivitis in kittens is plaque build-up. Plaque is a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If not removed, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which can lead to gum disease. Other causes of gingivitis in kittens include:
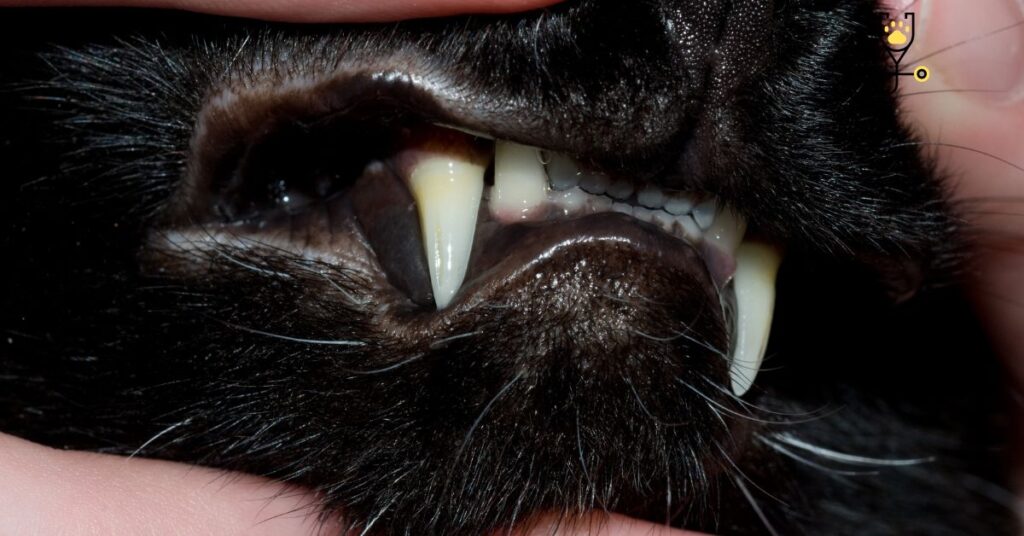
• Poor oral hygiene: If your kitten’s teeth are not brushed regularly, plaque can build up and lead to gingivitis.
• Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can cause inflammation of the gums.
• Foreign bodies: Objects caught between the teeth can irritate the gums and lead to gingivitis.
• Dental diseases: Certain dental diseases, such as feline tooth resorption, can cause gingivitis.
• Genetics: Some kittens are simply more prone to developing gum disease than others.
Symptoms of Gingivitis in Kittens
The most common symptom of gingivitis in kittens is bad breath. This is because the bacteria in plaque can cause a foul odor. Other symptoms of gingivitis include:
1. swollen gums: Gums may appear red, puffy, or inflamed.
2. bleeding gums: You may notice blood on your kitten’s teeth or gums when you brush their teeth or they eat.
3. decreased appetite: If your kitten’s gums are painful, they may not want to eat.
4. drooling: Some kittens with gum disease may drool more than usual.
5. pawing at the mouth: If your kitten is in pain, it may paw at its mouth or rub its face against something to try to relieve the discomfort.
6. lethargy: Gum disease can be painful and make your kitten feel tired and sluggish.
7. weight loss: If your kitten is not eating due to pain from gum disease, it may lose weight.
8. teeth loss: In severe cases of gum disease, teeth may fall out.
Treatment of Gingivitis in Kittens
If you suspect your kitten has gingivitis, it’s important to take them to the vet for a check-up. Your vet will be able to confirm the diagnosis and develop a treatment plan. The goal of treatment is to remove the plaque and tartar from your kitten’s teeth and gums and to reduce the inflammation. Treatment may include:
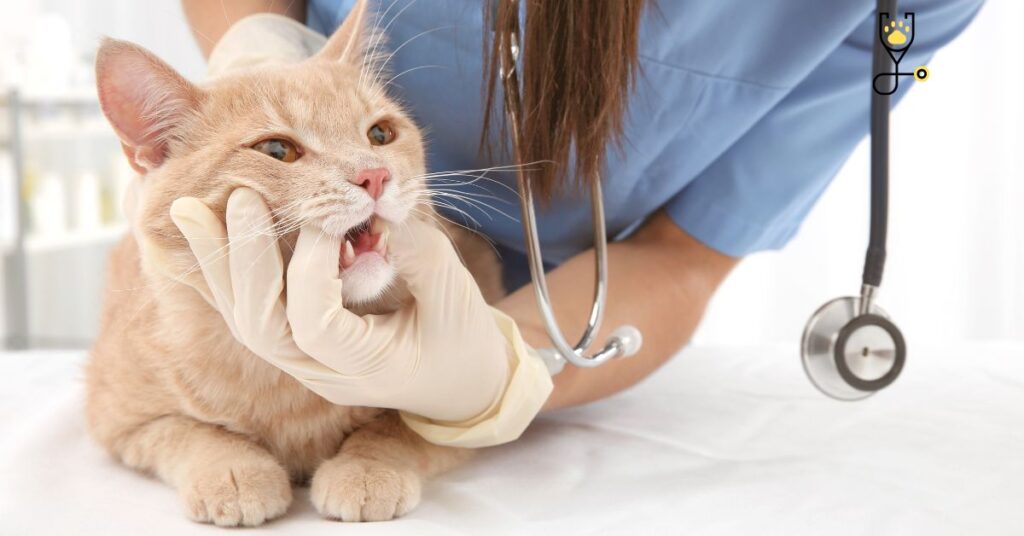

1. Professional dental cleaning: This is done under anesthesia and involves scaling and polishing your kitten’s teeth to remove plaque and tartar.
2. Antibiotics: If there is an infection present, your vet may prescribe antibiotics to clear
it up.
3. Pain relief: If your kitten is in pain, your vet may prescribe pain medication.
4. Home care: Your vet will likely recommend a home care plan that includes regular brushing, dental wipes or gel, and oral rinses.
5. Diet: Your vet may recommend a dental diet or treats to help reduce plaque build-up.
Preventions of Gingivitis in Kittens
The best way to prevent gingivitis is to brush your kitten’s teeth regularly. This will help remove plaque before it has a chance to harden into tartar. Other ways to prevent gingivitis include:
1. Dental diets and treats: There are specially formulated diets and treats that can help reduce plaque and tartar buildup.
2. Dental wipes and gel: These products can help remove plaque from your kitten’s teeth and gums.
3. Oral rinses: These can help reduce plaque and bacteria in your kitten’s mouth
rushing your teeth regularly, flossing, and using mouthwash.
4. Quit smoking: Smoking can increase your risk of developing gum disease. If you smoke, it’s important to quit to help protect your oral health.
5. Visit the dentist: Be sure to visit the dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups.
6. Practice good oral hygiene: In addition to brushing your teeth, be sure to practice good oral hygiene by
7. Avoid sugary foods and drinks: Sugar can promote plaque growth, so it’s important to limit sugary foods and drinks in your diet.
8. Get regular vet check-ups: Be sure to take your kitten for regular vet check-ups so that any dental problems can be caught early.
Diagnosing Gingivitis in Kittens

If you suspect your kitten has gingivitis, it’s important to take them to the vet for a check-up. Your vet will examine your kitten’s mouth and look for signs of plaque and tartar buildup. They may also take X-rays to check for any damage to the teeth or gums. A biopsy may also be done to rule out other conditions.
Gingivitis is a common condition that can affect kittens of all ages. It’s important to brush your kitten’s teeth regularly and visit the vet for regular check-ups to help prevent it. If your kitten does develop gingivitis, it’s important to get treatment right away to avoid further damage to their oral health.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a common condition that can affect kittens of all ages. If not treated, it can lead to more serious problems like tooth loss and infections. The best way to prevent gingivitis is to brush your kitten’s teeth regularly and visit the vet for regular check-ups. If your kitten does develop gingivitis, treatment is important to avoid further damage to their oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Gingivitis is a common condition that causes inflammation of the gums. If not treated, it can lead to more serious problems like tooth loss and infections.
The symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Your kitten may also have bad breath.
Your vet will examine your kitten’s mouth and look for signs of plaque and tartar buildup. They may also take X-rays to check for any damage to the teeth or gums. A biopsy may also be done to rule out other conditions.
The treatment for gingivitis will depend on the severity of the condition. Treatment options include dental cleaning, antibiotics, pain relief, home care, and diet changes.
The best way to prevent gingivitis is to brush your kitten’s teeth regularly and visit the vet for regular check-ups. Other ways to prevent gingivitis include feeding a dental diet, using dental wipes or gel, and giving oral rinses.